Have you ever worked so hard on a task only for it to get wasted cause technology failed you? Frustrating, isn’t it? Well, you are not alone.
Today, many companies heavily rely on technology to support critical operations, deliver services, and maintain productivity. However, this increasing reliance on technology comes with complexity, vulnerability, and complication. As such, the organization needs to build a resilient IT infrastructure.
So, in this article, we will explore eight strategies to help businesses build a resilient IT infrastructure that can adapt to changing needs and overcome challenges. Let’s dive in and discover how to make your IT infrastructure more resilient.
What is a Resilient IT infrastructure?
Before tackling the strategies, it is first essential to learn the definition of a resilient IT infrastructure.
A resilient IT infrastructure refers to a system that can withstand and recover from unexpected events or disruptions. It includes redundant systems, backup plans, and disaster recovery protocols.
The goal of a resilient IT infrastructure is to minimise downtime, maintain business continuity, protect data integrity, and ensure that critical operations can continue even in the face of adversity. After all, the main objective of this system is to give organisations the ability to withstand and adapt to disruptions, failures, and cyber threats while maintaining functionality and service availability.
With that said, the perfect resilient infrastructure should involve anticipating points of failure, human error, and technical support requirements. This is to ensure that critical infrastructure remains operational.
Why does a company need a resilient IT infrastructure?
A resilient IT infrastructure is crucial for businesses for several reasons.
First, it ensures high availability, enabling operations to continue uninterrupted, even during unexpected disruptions. This high availability is achieved through the implementation of disaster recovery and business continuity plans, which minimise downtime and data loss.
Secondly, investing in a resilient IT infrastructure is crucial for the private sector as it safeguards critical assets, data, and services. This is necessary to ensure continuous operation and delivery of service.
Third, having a resilient IT infrastructure is crucial in ensuring cybersecurity by providing several layers of defence against cyber threats. It helps minimise the impact of cyberattacks, ensure rapid recovery from incidents, and maintain the integrity and availability of critical systems and data.
Ultimately, investments in resilient infrastructure provide an indispensable foundation to support business growth and scalability. This enables organisations to quickly adapt to ever-changing market demands and stay ahead of the competition.
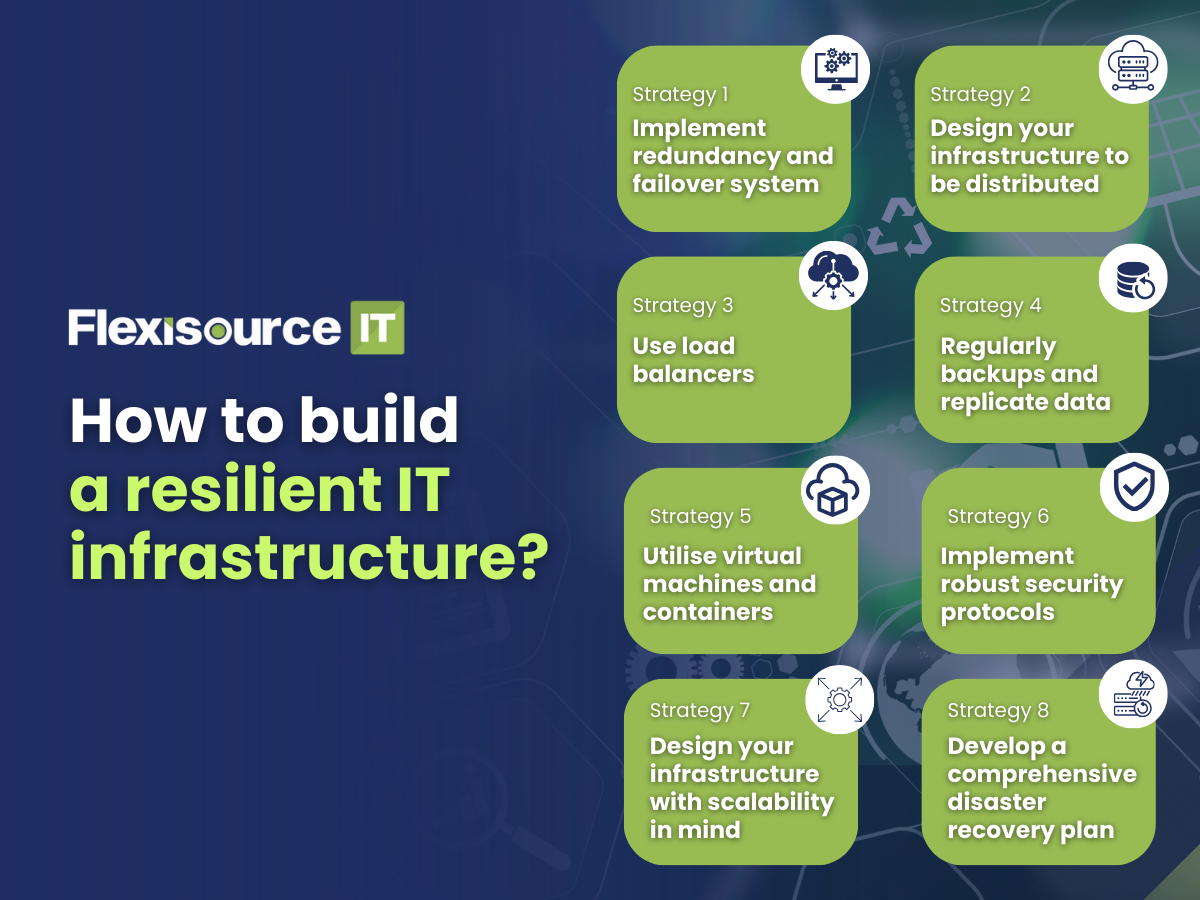
How to build a resilient IT infrastructure?
Building a resilient IT infrastructure is a multi-faceted process that requires careful planning, investment, and ongoing maintenance. To help you with that, here are eight strategies that might help you!
Strategy 1: Implement redundancy and failover system
First and foremost, redundancy and failover systems are essential to mitigate the impact of partial failures and cyber disruptions.
Redundancy refers to duplicating critical components or systems to ensure continuous operation. This minimises the risk of downtime in case of failures or disruptions. On the other hand, a failover system is a mechanism designed to automatically transfer the workload from a primary system to a backup or secondary system in case of a failure.
Implementing both these systems can enhance infrastructure resilience and high availability to a company. How so? These systems proactively alleviate single points of failure and safeguard against potential disruptions.
With that said, here are some tips for implementing redundancy and failure system mechanisms in your IT Infrastructure:
- Identify critical components in the system that need redundancy measures to be in place. These could include power supply units, network switches, storage devices, or servers.
- Test systems regularly for both planned and unplanned failovers to assess how well the system responds under different scenarios.
- Implement redundant hardware such as servers, storage devices, and network switches.
- Use clustering and mirroring techniques to ensure data redundancy.
Strategy 2: Design your infrastructure to be distributed
One of the most effective strategies for building resilience in infrastructure is designing a distributed system. Businesses can reduce the impact of partial failures and increase overall resilience by spreading infrastructure components across multiple locations.
Likewise, it also enables businesses to scale their operations more effectively by providing a flexible and adaptable platform that can handle increased traffic and demand.
With that said, several considerations are needed when designing a distributed infrastructure.
- Decentralise components and break down your infrastructure into smaller, independent components or services. Distribute these components across multiple servers, data centres, or cloud regions to reduce dependencies and increase fault tolerance.
- Utilise distributed storage systems such as distributed file systems, object storage, or NoSQL databases. These solutions allow data to be distributed across multiple nodes, providing scalability and fault tolerance.
- Implement distributed caching platforms like Redis or Memcached to enable data to be stored and accessed across multiple nodes. This can also improve performance and scalability by caching frequently accessed data closer to the user.
By investing in a distributed infrastructure design, businesses can significantly increase the resilience and availability of critical applications and services. This not only minimises the risk of disruptions but also ensures that companies are prepared for any potential disasters or emergencies.
Strategy 3: Use load balancers
Comparatively, load balancers are systems that distribute network traffic across multiple servers to improve performance, availability, and reliability. It significantly improves the resilience of IT infrastructure, particularly in managing high traffic volumes and distributing it effectively.
To illustrate, load balancers use different algorithms to assign server requests, such as round robin, least connections, or hash. It monitors the health and capacity of servers and adds or removes them as needed.
With that said, here are some crucial strategies to consider when using load balancers:
- Consider using load balancer tools that distribute incoming traffic across multiple backend servers.
- Configure load balancers to monitor the health of backend servers continuously and reroute traffic away from servers that experience issues.
- Consider response time and latency to provide the best possible user experience.
- Implement load balancing algorithms such as round-robin, least connections, or the least response time.
- Regularly assess load balancer performance and conduct load testing to ensure they meet service-level agreements (SLAs) and can handle expected traffic loads.
Strategy 4: Regularly backups and replicate data
Correspondingly, regular backups and data replication are essential for protecting against data loss due to hardware failures, software bugs, or cyberattacks. When implementing backup and replication strategies, consider the following:
- Establish a backup schedule based on the criticality of data and recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs).
- Use a combination of full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups to balance data protection and storage efficiency.
- Store backups offsite or in the cloud to protect against onsite disasters such as fires, floods, or theft.
- Test backup and recovery procedures regularly to ensure data integrity and reliability.
Strategy 5: Utilise virtual machines and containers
In the same way, virtual machines (VMs) and containers are both technologies that are critical components of the modern IT environment. VMs are suited for running multiple operating systems or heavier workloads with splendid isolation. While containers are ideal for lightweight, portable application deployment and scalability.
With that in mind, VMs and containers can significantly create a resilient IT infrastructure. Both of these technologies offer isolation, which helps contain faults and prevent them from affecting other parts of the infrastructure. If one VM or container fails due to a hardware or software issue, it typically doesn’t impact others.
When it comes to utilising VMs and Containers, several strategies can be employed, such as the following:
- Deploy new VM instances to ensure that workloads continue running even in the event of failure.
- Build redundancy into your architecture to help mitigate risk by providing backup systems or resources that can take over if needed.
- Automate everyday tasks to reduce human error in VMs and containers
- Implement comprehensive monitoring and alerting systems to continuously monitor the health and performance of VMs, containers, and underlying infrastructure components.
- Design VM and container environments to be scalable and elastic, allowing resources to be dynamically allocated or deallocated based on workload demands.
Strategy 6: Implement robust security protocols
In IT, security is a critical aspect of resilience planning. A robust security system can help protect the infrastructure from cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and attacks. There are several strategies that organisations can adopt to enhance their security and resilience, such as the following:
- Implement robust security protocols like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption to prevent unauthorised access and data breaches.
- Regularly update security measures by patching applications to reduce the risk of exploitation by cybercriminals.
- Conduct routine security assessments and penetration testing to identify weaknesses in the infrastructure.
- Train employees on cybersecurity best practices such as safe browsing, password security, and data protection.
- Implement monitoring and logging systems to detect and respond to security incidents promptly.
Strategy 7: Design your infrastructure with scalability in mind
Incorporating scalability in infrastructure design is vital. It supports reliance, automation, and scalability, reducing latency and configuration issues. Likewise, scalability is essential for accommodating growth and fluctuations in demand without compromising performance or reliability.
Following that, try to consider the following when designing a scalable IT infrastructure:
- Choose scalable hardware and software solutions that can easily accommodate increases in workload and traffic.
- Implement auto-scaling techniques to add or remove resources automatically based on demand.
- Use cloud computing services such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud to leverage on-demand resources and elastic scaling.
- Monitor performance metrics and trends to anticipate future resource requirements and plan accordingly.
Strategy 8: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan
Last but not least, Disaster Recovery Plans (DRP). DRP is a critical aspect of protecting data and applications in unforeseen events. Having said that, a resilient infrastructure requires a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that accommodates various failure scenarios and considers the impact of downtime on critical applications and data.
So, to develop a comprehensive DRP, try the following:
- Identify critical systems and data that require protection and prioritise recovery efforts accordingly.
- Establish recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) to guide recovery efforts and minimise downtime.
- Implement backup and replication strategies to ensure data availability and integrity during a disaster.
- Document and test recovery procedures regularly to verify their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
To summarise, building a resilient IT infrastructure is crucial for all businesses. It ensures the smooth functioning of safeguards against potential threats and disruptions. That’s it! I hope the above-mentioned strategies will help you develop and strengthen your IT infrastructure.
If you’re unsure where to start or need expert guidance, contact Flexisource IT for a free consultation with our IT specialists. We will evaluate your infrastructure needs and explore how we can help you build a resilient IT environment. Protect your business and build a resilient IT infrastructure today!









